Curious about advancements in heart therapy? Learn how CRT is revolutionizing care.
A Brief History of CRT Development
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is a transformative approach in the management of heart failure, particularly for patients whose hearts pump out of sync. This transformative technology has significantly improved patient outcomes and heart function, and its rapid evolution continues to offer new possibilities in cardiac care.
The concept of CRT emerged from the understanding that heart failure is not only a problem of muscle weakness but also of poor coordination in the heart’s electrical system. Early CRT systems were developed in the 1990s, initially using pacemaker technology to correct dyssynchrony in the lower chambers of the heart. Over the years, these systems have evolved from basic pacing functions to sophisticated devices capable of managing complex heart rhythms and incorporating defibrillator functions to prevent sudden cardiac death.
How CRT Systems Work
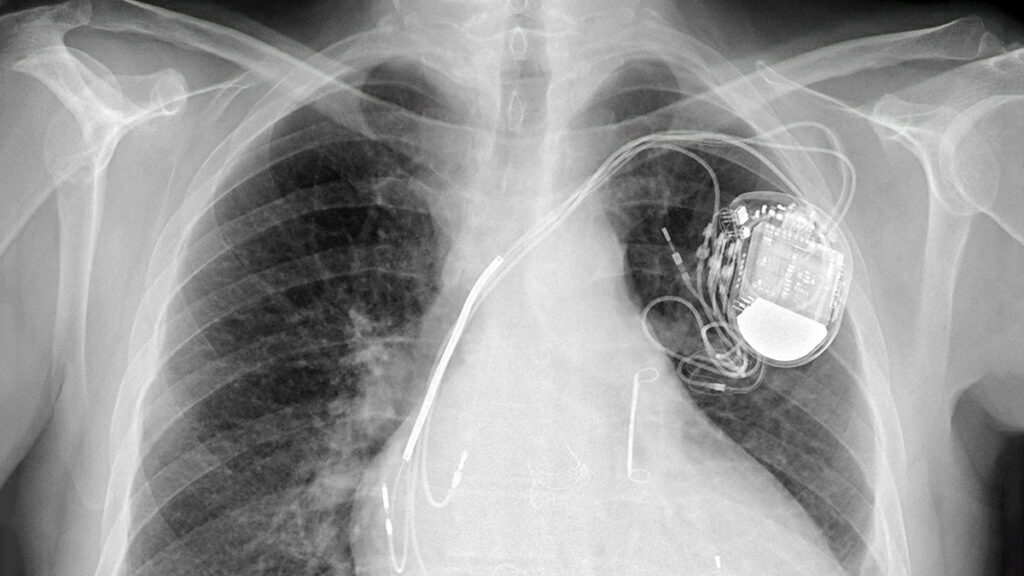
CRT devices are designed to deliver small electrical impulses to both the left and right ventricles, helping them contract more uniformly and effectively. This synchronization improves the efficiency of the heart’s ability to pump blood and oxygen throughout the body, which can significantly improve symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue. The CRT devices are implanted under the skin, typically just below the collarbone, with leads running to the heart.
Key Benefits of Advanced CRT Systems
Modern CRT systems offer several benefits:
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Patients often experience a remarkable improvement in their ability to perform daily activities without the debilitating symptoms of heart failure.
- Reduction in Hospitalizations: Proper synchronization can decrease the need for hospitalizations due to heart failure exacerbations.
- Increased Survival Rates: Studies have consistently shown that CRT improves survival rates among patients with severe symptoms of heart failure who do not respond to medical therapy alone.
Detailing the Treatment Process
The implantation of a CRT device is a procedural method that shares similarities with pacemaker insertion but is distinguished by its specific approach and objectives. Here’s a streamlined overview of the process:
- Preparation and Pocket Formation:
Prior to the implantation of a CRT device, patients undergo detailed pre-operative assessments to ensure they are suitable candidates for the procedure. These assessments may include various imaging studies to help accurately guide the placement of the leads. Once suitability is confirmed, the surgical team proceeds to make an incision under the skin, typically just below the collarbone. This incision is used to create a small pocket where the CRT device will be securely placed.
- Lead Placement:
Three leads are typically involved in the CRT setup:
- Right Atrial Lead: This lead is inserted to help coordinate the timing of the atrium’s contractions, ensuring that the upper chambers of the heart beat in sync with the lower chambers.
- Right Ventricular Lead: Placed directly in the right ventricle, this lead is essential for the synchronization of the ventricles, the main pumping chambers of the heart.
- Left Ventricular Lead: Depending on the specific anatomical and physiological needs of the patient, this lead is placed either through the coronary sinus or via a left-bundle branch access. The placement of this lead is particularly important as it helps optimize the contraction of the left ventricle, crucial for effective heart function.
- Device Settings Adjustment and Initial Testing:
After the leads are placed, the CRT device settings are carefully adjusted to ensure the heart rhythm is optimally synchronized. This meticulous adjustment is tailored to the individual’s specific cardiac needs and is critical for the device to function effectively. The device is then tested to confirm correct lead placement and optimized heart synchronization.
- Regular Follow-Up:
A wound-check is typically performed within the first week after implantation to assess for complications, such as signs of infection at the implantation site. Regular follow-up visits are a crucial component of post-implantation care, as well. During these visits, the performance of the CRT device is monitored, and any necessary adjustments are made. These sessions help address any potential issues such as lead displacement or changes in the patient’s cardiac condition, ensuring the long-term success of the therapy.
Understanding Recovery and Expectations
Recovery from a CRT implantation involves limited physical activity for several weeks to allow the leads to stabilize and integrate with the body. Some patients who undergo CRT implantation may already have a pacemaker or ICD system that will be upgraded or replaced, so the recovery process should resemble their initial implantation. Patients are typically able to return to their normal activities gradually, with improvements in heart function and symptoms noted within a few months. It is important for patients to engage in regular follow-up care to ensure the device functions optimally.
Addressing Limitations and Considerations
While CRT is a life-altering treatment for many, it is not suitable for all heart failure patients. Success depends on specific patterns of heart failure and the presence of cardiac dyssynchrony. Furthermore, complications such as lead displacement or infection, while rare, do occur and require prompt management. It is crucial for patients to adhere strictly to medical advice, engage in regular visits with their physician, and integrate discussed practices into their daily lives to manage their condition effectively.
The Conclusion on CRT
The evolution of CRT systems represents a significant leap forward in cardiac care, offering hope and improved quality of life for many heart failure patients. As technology advances, the integration of more sophisticated diagnostics and therapeutics holds the promise of even greater enhancements in patient care.
For patients struggling with heart failure symptoms or healthcare providers looking for advanced treatment options, exploring the potential of CRT is a worthwhile step. Consulting with a specialized cardiologist like Dr. Adam Budzikowski can provide deeper insights and personalized care plans. Book a consultation with him today to take a pivotal step towards optimal heart health.
CRR